ORIGINAL ARTICLES
What is already known about thе subject?
► Nosocomial pneumonia is considered one of the most severe infectious diseases in healthcare facilities
► Antibacterial resistance of pathogens responsible for hospital-acquired infections significantly complicates the choice of therapy and forces the use of a large number of broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs (ABDs)
► Current clinical and economic evaluations of using systemic ABDs in real clinical practice are scarce due to the complexity of conducting such evaluations
What are the new findings?
► The clinical and economic effectiveness of using ABDs as a therapy for nosocomial pneumonia in hospital settings was evaluated
► An analysis of direct medical costs associated with ESKAPE group pathogens was conducted based on real-world data
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The obtained data could be used to rationalize antibiotic therapy and plan the hospital antimicrobial formularies
► The results of the study will aid in optimizing the expenditures of health-
care organizations, considering the high costs of systemic antibacterial therapy and microbiological monitoring of infectious pathogens
Objective: To conduct a clinical and economic analysis of antibacterial therapy for severe nosocomial pneumonia within the context of real clinical practice at a multidisciplinary hospital in Moscow.
Material and methods. The medical records of patients admitted to Yudin City Clinical Hospital in Moscow in 2019–2021 were analyzed retrospectively. Pharmacoepidemiological analysis included the structure of prescriptions of antibacterial drugs (ABDs), features of empirical and etiotropic therapy, duration of using ABDa and other parameters. In total, 110 cases of severe nosocomial pneumonia caused by ESKAPE pathogens were selected for analysis. Direct medical costs and cost-effectiveness coefficients were calculated based on real world data.
Results. It was established that nosocomial pneumonia is the most common complication among hospitalized patients in the intensive care unit (ICU). The etiology of nosocomial pneumonia was mostly presented by K. pneumoniae, A. Baumanii, and P. aeruginosa. The administered ABDs included 31 international nonproprietary names of the group J01 Systemic antibacterial drugs. The direct medical costs of empirical antibacterial therapy averaged for 9367 rubles (2118 rubles [1462; 3525]). Comparative cost-effectiveness analysis was performed based on surrogate and endpoints. It was found that direct medical costs associated with ESKAPE pathogens spend about 70% of the budget of established tariff to pay for medical care of the compulsory health insurance program for the patient's stay in the ICU.
Conclusion. Antibacterial therapy costs for nosocomial pneumonia significantly increase the total cost of a patient's hospital stay. Сlinical and economic assessment of drug use help optimize therapy costs and develop a hospital formulary of antimicrobial drugs.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Medicines for the treatment of rare diseases are characterized by a high level of uncertainty regarding their clinical efficacy
► For decision-making on the reimbursement of medicines intended for the treatment of children with severe life-threatening, including rare, diseases, various clinical, economic, and social factors should be taken into account
What are the new findings?
► An analysis of medicines and diseases for which health technology assessments were performed for their inclusion in the lists of the “Circle of Kindness” Foundation during the period from February 1, 2021 to December 31, 2024 was conducted
► Medicines and diseases included in the lists of the “Circle of Kindness” Foundation are characterized by a high unmet medical need (absence of alternative treatment options) and, in more than half of the cases, by the corresponding orphan status in the EU and/or USA
► In clinical efficacy studies of the medicines, the predominant use of surrogate endpoints, assessment of results over an average outcome assessment time horizon of 12 months from the start of therapy, and the absence of comparative data in one-third of the cases were noted
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Inclusion of medicines in the procurement lists of the “Circle of Kindness” Foundation and the analysis of related patterns contribute to improving the quality of medical care for children
► Health technology assessment and financing , particularly for unregistered medicines, allow patients to access innovative medicines earlier, thereby increasing both the duration and quality of their life
Background. In 2021, the Russian Foundation “Circle of Kindness” was established to provide additional financial support for children with severe life-threatening and chronic diseases (including rare and orphan ones) requiring essential treatment, particularly expensive medicines. At the same time, the predominant part of the provided medicines is intended for the treatment of rare diseases. Methodological support for decision-making regarding the inclusion of diseases in the list of diseases and medicines in the procurement lists of the “Circle of Kindness” Foundation is provided by health technology assessment conducted in the Center for Healthcare Quality Assessment and Control.
Objective: To analyze the characteristics of medicines that underwent assessment during the four years of operation of the “Circle of Kindness” Foundation, depending on their inclusion status in the procurement lists, as well as to review the evidence base confirming the clinical effectiveness of the analyzed medicines.
Material and methods. A total of 187 pairs of “medicine – disease” that underwent assessment were analyzed based on the following characteristics: registration status of the medicines in the Russian Federation, the United States of America (USA), and the European Union (EU), and data on orphan status for registered technologies; the presence of unmet therapeutic needs for the given medicine (absence of alternative therapy options); and data on the availability of generic medicines. Characteristics of published studies on the clinical efficacy of the medicines included in the analysis contained information on study design, used endpoints (surrogate or clinical outcomes), median follow-up duration, control group, as well as the presence of comparative studies for each “medicine – disease” pair.
Results. It was found that medicines included in the procurement lists, compared to the analyzed non-included medicines, were characterized by a higher frequency of obtaining orphan status in the USA (84.6% vs. 67.8%) and the EU (65.7% vs. 38.8%) as well as by the absence of alternative therapy options (50.6% vs. 32.0%). Use of surrogate endpoints only was reported in 56% of published studies on the clinical efficacy of the medicines; the median time follow-up for outcome assessment was 12.00 months (interquartile range 5.52–35.94). Among study designs, randomized controlled trials and single-arm studies predominated (36.7% and 30.9%, respectively). Published data on the results of comparative studies were absent for 36.8% of all analyzed “medicine – disease” pairs.
Conclusion. Pairs of “medicine – disease” included in the “Circle of Kindness” Foundation lists are characterized by a high unmet medical need (absence of alternative treatment options) and, in more than half of the cases, by the corresponding orphan status in the EU and/or USA. The obtained results also correspond to data from domestic and international authors regarding the predominant use of surrogate endpoints and the prevalence of single-arm study designs justifying the efficacy of orphan medicines. These findings highlight the relevance of conducting health technology assessments of medicines with high uncertainty regarding their effectiveness, which, on the one hand, allows for consideration of the limitations of evidence from their clinical studies, and on the other hand, summarizes data on other significant characteristics of the medicines and rare diseases.
What is already known about thе subject?
► The cost of anticancer drug therapy (ACDT) places unprecedented financial pressure on healthcare systems worldwide
► Modern studies demonstrate that the high cost of innovative anticancer drugs does not always correlate with meaningful clinical outcomes
► The combined ABC/VEN analysis, as a method of clinical and economic evaluation, is an effective tool for the comprehensive assessment of both the financial burden (ABC) and clinical significance (VEN) of ACDT
What are the new findings?
► Disproportions were identified in the funding structure of ACDT, which are characteristic of modern pharmaceutical supply systems with emphasis on financing targeted therapy options
► The inclusion of drugs of the same type in different categories during ABC analysis may indicate the existence of "budget" alternatives and underutilization of more affordable and equivalent drugs, such as generics and biosimilars, when available
► The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines for classifying drugs into VEN categories includes only those drugs that have shown significant survival benefits or have met the WHO-established threshold of efficacy, thereby limiting the evaluation of drugs that have not demonstrated such priorities
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The findings underscore the necessity of developing an adaptive pharmaceutical supply system that takes into account both the clinical significance of medicines and the economic efficiency of their use
► Maintaining full patient access to effective treatment is an unquestionable priority in oncology practice and requires strict assessment of objective measures for improvements in quality and duration of life
► One potential solution is a multicriteria evaluation system for anticancer drugs that takes into account clinical efficacy, social significance, pharmacoeconomic parameters, and other factors that impact the healthcare system as a whole
Background. Modern oncology is facing a paradoxical situation in which the rapid increase in the cost of anticancer therapy is not always accompanied by a proportional improvement in its effectiveness. This creates serious economic barriers for healthcare systems worldwide. In the context of limited resources, methods for the rational allocation of the pharmaceutical budgets are becoming particularly important. The combined ABC/VEN analysis serves as an effective tool to address this challenge. This approach is especially valuable when analyzing contemporary oral anticancer drugs, which are playing an increasingly significant role in cancer treatment.
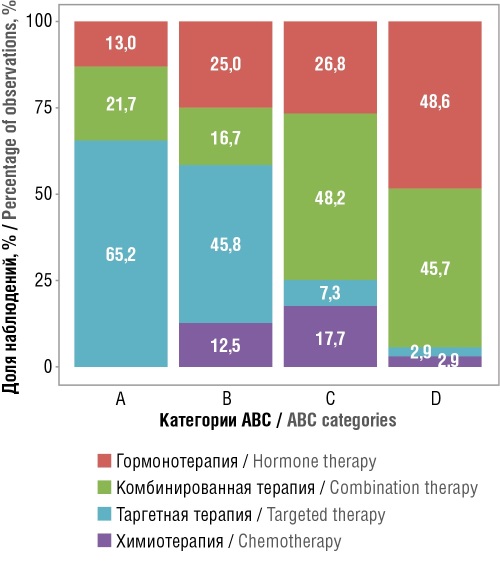
Objective: To evaluate the cost structure of oral anticancer therapy using ABC/VEN and frequency analysis methods.
Material and methods. Distribution by ABC categories was conducted according to generally accepted methodology. Group A (the most expensive drugs) included regimens whose total cost accounted for 80% of all expenditures. Group C (the least expensive) comprised regimens with no more than 5% of total costs. The remaining regimens formed Group B (moderately expensive), which consumed 15% of total expenditures. Final expenditures were determined based on the cost of drug therapy per regimen in a day hospital setting and the number of medical interventions provided under each regimen in 2022. The formal methodology of VEN analysis involved categorizing regimens according to the presence of drugs from the World Health Organization Model List of Essential Medicines. Separately, both ABC and VEN analyses were carried out for chemotherapy, hormone therapy, targeted therapy, and combination treatment regimens. Frequency analysis was conducted based on the number of hospitalizations of patients who received particular anticancer regimens according to real-world data from depersonalized hospitalization registry records.
Results. The resource distribution analysis confirmed the Pareto principle, with 80% of financial expenditures attributed to 9.3% (95% CI 6.0–13.7) of therapeutic regimens (23 regimens) constituting the high-cost Group A. Group C (accounting for no more than 5% of expenditures) included 164 regimens (66.7%; 95% CI 60.4–72.5). The remaining drugs fell into Group B (15% of expenditures) – 24 regimens (9.8%; 95% CI 6.4–14.2). Meanwhile, 35 regimens (14.2%; 95% CI 10.1–19.2) were not used in 2022. The distribution of regimens by VEN groups was consistent with recommendations: 149 regimens (60.6%; 95% CI 54.2–66.7) for Group V, 63 regimens (25.6%; 95% CI 20.3–31.5) for Group E, and 34 regimens (13.8%; 95% CI 9.8–18.8) for Group N. The combined ABC/VEN analysis demonstrated that Group A predominantly included drugs from Group V (52.2%). However, it also revealed disproportions: a significant proportion (39.1%) of Group N drugs in Group A requires special attention and indicates the need for mechanisms to regulate the prescription of high-cost drugs.
Conclusion. The findings provide a foundation for developing balanced approaches to pharmaceutical provision in oncology, combining the principles of clinical appropriateness and economic efficiency. The study justifies the need for resource allocation strategies that ensure the priority provision of evidence-based treatment regimens in the context of limited resources.
What is already known about thе subject?
► In the consumption structure of antihypertensive drugs (AHDs) in the Russian Federation (RF), single-ingredient drugs predominate, while statin use among the population remains at a low level
► The volumes and structure of pharmacy sales of AHDs and statins over the past 6 years across 83 of the 89 regions of the RF have not been previously studied
What are the new findings?
► The presented data on the sales structure of key cardiovascular drugs (AHDs and statins) in 5,200 pharmacy organizations is representative of 7 federal districts and of the Russian Federation as a whole
► A low share of fixed-dose combinations (FDCs) of AHDs and statins in the consumption structure of key cardiovascular drugs among the population was identified, along with a lack of significant growth in their use in recent years
► It was shown that the low cost of single-ingredient drugs is the main factor driving their predominant use among the population
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The presented data provide a reliable basis for studying the dynamics of pharmacy sales of drugs under consideration in the RF
► The efforts are required to increase the use of statins and AHDs in accordance with key trends in cardiology
► The obtained results highlight the need to reduce the cost of AHD FDCs
Background. In the modern population, cardiovascular diseases associated with arterial hypertension and dyslipidemia predominate in the structure of non-communicable diseases, which justifies the need for long-term pharmacotherapy with antihypertensive and lipid-lowering drugs.
Objective: To study the consumption profile of antihypertensive and lipid-lowering drugs by the population of the Russian Federation (RF), which can be considered key cardiovascular drugs.
Material and methods. A long-term retrospective pharmacoepidemiological study was conducted. The statistics of pharmacy sales of these drug groups were analyzed, both as single-ingredient drugs and as fixed-dose combinations (FDCs), from 2017 to 2022 across 5,221 pharmacy organizations in 83 regions of the RF, out of a total of 70,400 pharmacy organizations registered in the country in 2022.
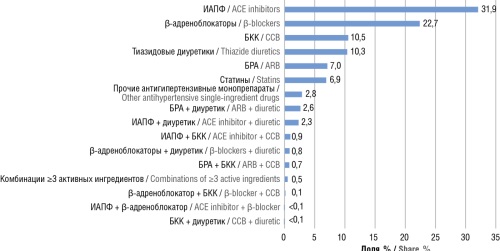
Results. It was found that the consumption of the following single-ingredient drugs predominates: angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (31.9%), β-blockers (22.7%), calcium channel blockers (10.5%), and diuretics (10.3%). Among single-ingredient drugs, the leading positions are held by amlodipine (13.6%), enalapril (11.6%), and indapamide (9.7%). Among FDCs, the most common are “losartan + hydrochlorothiazide” (20.6%), “perindopril + indapamide” (15.4%), “amlodipine + indapamide + perindopril” (9.1%). Average cost of 1 defined daily dose (DDD) was 2.8 rubles for diuretics, 3.2 rubles for calcium channel blockers, 4.0 rubles for angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, 8.0 rubles for sartans, 10.0 rubles for β-blockers, 9.0 rubles for statins. The cost of 1 DDD for FDCs is significantly higher – ranging from 15 to 40 rubles – which may be a key factor contributing to their extremely low consumption (7.1% for antihypertensive FDCs and 6.9% for statin FDCs), inconsistent with current clinical guideline recommendations.
Conclusion. The structure of pharmacy sales of key cardiological drugs from 2017 to 2022 has remained conservative, with a predominance of single-ingredient medications and a lack of alignment with current cardiology trends toward increased use of FDCs and statins. To date, no domestically produced polypill formulations combining an antihypertensive agent and a statin exist on the Russian market, and the share of imported polypill multitarget drugs remains extremely low.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Historically, there has been a discrepancy in the Russian Federation between the theoretical need for the use of angiogenesis inhibitors and their actual level of consumption in patients with age-related macular degeneration
► The latest data on the use of angiogenesis inhibitors date back to 2019, which justifies the need to update information on their current use within the healthcare system
What are the new findings?
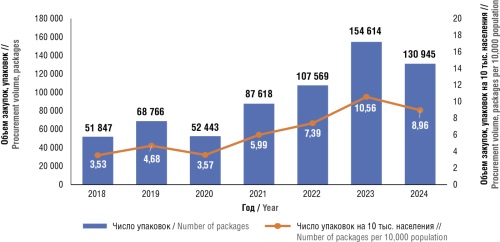
► The data on the range of angiogenesis inhibitors, maximum selling prices, actual prices, procurement and consumption volumes for the period from 2018 to 2024 were updated
► A positive trend in the provision of this group of drugs was identified. An overall increase in procurement, including indicators of more expensive representatives of the group, was noted
► Calculations indicate that a single vial of an angiogenesis inhibitor drug is used for multiple patients, which does not comply with their medical use instructions
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The results of the study can be used to improve the system of pharmaceutical care for patients with age-related macular degeneration
► The obtained data may serve as a basis for manufacturers and suppliers of angiogenesis inhibitors to expand the supply of this group of drugs
► The need to address the issue of using a single vial of angiogenesis inhibitor for multiple patients was underlined
Background. Studies on the pharmaceutical provision of neovascular age-related macular degeneration with angiogenesis inhibitors in the Russian Federation have repeatedly indicated a mismatch between the level of consumption and the actual need for these drugs. This highlights the importance of further research on the issue through marketing analysis.
Objective: To conduct a marketing analysis of the market for angiogenesis inhibitors used in the treatment of neovascular age-related macular degeneration, including assessment of the product range, price dynamics, demand and consumption, as well as index analysis for the period of 2018–2024.
Material and methods. The study was based on open data on the procurement of angiogenesis inhibitors in the public sector, price characteristics, and information on consumption with compulsory health insurance system (24-hour and day hospitals as well as high-tech medical care). The scientific and methodological framework of the study included methods for analyzing the sales of drugs from the group of angiogenesis inhibitors registered for medical use in the Russian Federation, as well as methodological tools for calculating a series of chain indices (including the weighted average price index, price index, structural shift index, index of changes in sales volumes in physical terms, modified Herfindahl–Hirschman index). Methods for analyzing the life cycle of the drugs and comparing the volumes of their procurement and consumption volumes were also used.
Results. During the study period, there was a noticeable increase in the demand for and consumption of angiogenesis inhibitors: procurement volumes in physical terms grew 2.53-fold, and in monetary terms 1.62-fold. The positive dynamics of the market for the studied group of drugs were accompanied by an increase in weighted average prices and a growing share of more expensive drugs in the procurement structure. Between 2021 and 2023, uneven growth was observed in procurement volumes in physical terms and in the number of hospitalizations involving the use of these drugs. The ratio of hospitalization volumes to procurement volumes during this period was 1.21, 1.46, and 1.47, respectively, indicating that a single vial of the drug was used for multiple patients. The disproportion between procurement volumes and the number of hospitalizations points to a significant additional potential demand for angiogenesis inhibitors. The current market conditions can be characterized as attractive for manufacturers and suppliers.
Conclusion. It was established that the market for angiogenesis inhibitors was characterized by both qualitative and quantitative growth, with sustained positive development dynamics. The identified features of procurement and consumption indicate the need for further research aimed at developing optimal solutions for ensuring the pharmaceutical provision of angiogenesis inhibitors to consumers in the required range and sufficient volumes.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (ω3-PUFAs) have been studied as cardioprotective, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective agents and are widely used in pharmacology and nutrition science for the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases
► The fatty acid compositions depend on the source: marine fish are rich in eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), plant oils contain alpha-linolenic acid, algae provide a stable source of DHA
► The preparations differ in PUFA concentration, degree of esterification (triglycerides or ethyl esters), level of purification, and the presence of additional antioxidants that affect stability
What are the new findings?
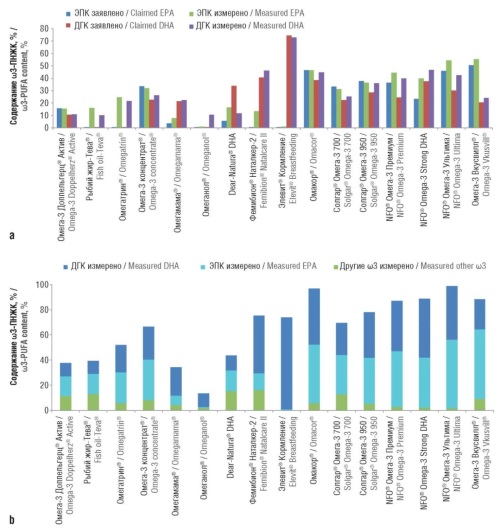
► A study of the fatty acid composition of 16 ω3-PUFA preparations was conducted, including quantitative chromatographic determination of more than 50 fatty acids, their derivatives, and other compounds
► Previously identified pharmacomarkers of fatty acid composition were confirmed, and new ones were identified that allow for highly reliable differentiation of preparations with a high degree of ω3-PUFA standardization
► New, more effective criteria for assessing the quality of the fatty acid composition of ω3-PUFA preparations were proposed. In particular, the compliance with the criteria “ω11<3%” and “EPA+DHA>55%” corresponds to more standardized preparations with better purification quality
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Using the data obtained in the study, physicians will be able to select more standardized ω3-PUFA preparations with proven composition and stability
► Personalized selection of ω3 preparations for patients with various pathologies will improve
► A basis will be established for incorporating new quality criteria into pharmacopoeias and guidelines
Background. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (ω3-PUFA) are an important factor in somatic and reproductive health. Micronutrient and pharmaceutical preparations based on ω3-PUFA are widely used for cardioprotection (prevention of atherosclerosis, endothelial dysfunction, chronic inflammation, and excessive thrombosis), support of reproductive function during pregnancy and improvement of neurological development in children. The effectiveness of ω3-PUFA preparations is determined by their fatty acid composition: the amounts of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and other types of unsaturated and saturated fatty acids.
Objective: To analyze the fatty acid composition of micronutrient and pharmaceutical ω3-PUFA preparations.
Material and methods. The fatty acid composition of 16 ω3-PUFA preparations was analyzed. A quantitative chromatographic method was used to determine more than 50 fatty acids, their derivatives, and other compounds.
Results. Previously identified pharmacomarkers of fatty acid composition were confirmed, and new ones were obtained, that allow for highly reliable differentiation between highly standardized ω3-PUFA preparations (such as Omacor®, NFO® Omega-3 Premium, NFO® Omega-3 Strong DHA, NFO® Omega-3 Ultima, etc.) and less standardized products (Fish oil-Teva®, Omeganol®, etc.). New, more effective criteria for assessing the quality of the fatty acid composition of ω3-PUFA preparations were proposed. In particular, compliance with the criteria “ω11<3%” and “EPA+DHA>55%” corresponds to more standardized preparations with better purification quality. The usefulness of our proposed standardization coefficient for evaluating the conformity of measured ω3-PUFA levels to the amounts claimed by manufacturers was confirmed.
Conclusion. Compliance with the criteria “ω11<3%” and “EPA+DHA>55%” corresponds to more standardized preparations. The identification of highly standardized compositions allows physicians and patients to make informed choices when selecting ω3-PUFA products.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Value-based healthcare (VBHC) is a model of medical care that evaluates the balance between clinical outcomes, patient-relevant outcomes, and economic costs
► Effective implementation of VBHC requires strict standardization of indicators as its absence hinders objective analysis and improvement of care quality
► To standardize the assessment of medical care, the International Consortium for Health Outcomes Measurement (ICHOM) develops unified sets of indicators that integrate outcomes important for VBHC; however, limited awareness of this resource among researchers limits its application in scientific studies
What are the new findings?
► The process of implementing VBHC was structured by systematizing methodological approaches to data collection and analysis according to ICHOM recommendations
► The results confirm that the developed data structure meets VBHC criteria, enabling comprehensive analysis of medical care based on clinical outcomes and patient-reported indicators
► The unification of data collection approaches through international standards ensures objective measurement of healthcare effectiveness and creates a unified conceptual framework for all stakeholders in the healthcare system
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The obtained results have significant practical value for implementing VBHC principles in clinical practice, providing a methodological foundation for standardized assessment of healthcare effectiveness
► The next step in this direction should be the adaptation of data collection for specific sets, taking into account national characteristics and the capabilities for conducting VBHC research in Russia
Background. Value-based healthcare (VBHC) is a model of medical care that focuses on analyzing treatment outcomes and takes into account patient-relevant results (values), clinical effectiveness, and economic costs. Although standardized assessment systems exist, such as those developed by the International Consortium for Health Outcomes Measurement (ICHOM), their practical application remains limited, slows the implementation of VBHC. The lack of unified methodologies reduces data comparability between healthcare organizations, hinders the identification of best practices, and ultimately impedes the practical realization of VBHC.
Objective: To analyze and adapt standardized approaches for assessing VBHC parameters and the methodologies for their collection based on ICHOM sets.
Material and methods. A comprehensive analysis was conducted on 49 ICHOM Standard Sets and 43 related publications in peer-reviewed journals. A structured study of the research objects was carried out, and potential barriers to the implementation of data collection methodologies by healthcare organizations were identified. Methods of qualitative content analysis and comparative data analysis were applied.
Results. The article presents a structure of indicators for the assessment of VBHC. Particular attention is given to three key components of outcomes assessment: patient-oriented outcomes – patient-reported outcomes, clinical outcomes, and indicators of healthcare resource utilization. Standardized approaches to data collection were identified, each of which has its own limitations. Optimal monitoring timelines were determined, varying depending on the type of nosology. The results demonstrate that ICHOM standards provide a comprehensive framework for assessing value-based healthcare; however, they require adaptation to specific organizational conditions. The developed data categorization and presented conclusions provide a foundation for healthcare institutions to initiate the implementation of a value-based approach, with a focus on outcomes that matter to patients.
Conclusion. The conducted analysis justifies the necessity of value-based healthcare research in accordance with the unified ICHOM Standard Sets. A unified methodology can provide a comprehensive and objective assessment of care effectiveness and foster a common understanding of the concept among all stakeholders. This approach will facilitate the transition from theory to global practice in value assessment in medicine. The next step in this direction should be the adaptation of data collection for specific sets, taking into account national characteristics and capabilities in Russia.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Cosmetics represent a product group in the pharmaceutical market within pharmacy sales, which is subject to less strict government regulation compared to medicinal products
► When sold in pharmacies, cosmetics are positioned as high-quality and safe. In 2022, the sales volume of cosmetics in pharmacies reached a record 50 billion rubles, making this product group significant in the sales structure of pharmacy chains
► With the introduction of anti-Russian sanctions, imports of foreign cosmetics declined, creating opportunities for the growth of domestic brands
What are the new findings?
► An assessment of the presence of dominant groups in the three cosmetics segments within pharmacy sales was carried out using the strength/variety matrix
► The selective cosmetics segment, characterized by the most expensive products, is the most concentrated. The dominant group, consisting of foreign brands, falls within the “natural oligopoly” quadrant
► The mass-market and active cosmetics segments are competitive, as no dominant group has been identified in recent years. A significant strengthening of positions of certain domestic brands has been observed
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► In segments where domestic brands are successfully growing, the replacement of foreign cosmetic products with more affordable Russian alternatives will become increasingly noticeable
► In the selective cosmetics market, where foreign brands dominate, products will become less accessible for consumers, which may lead to an increase in the cost of dermatological care
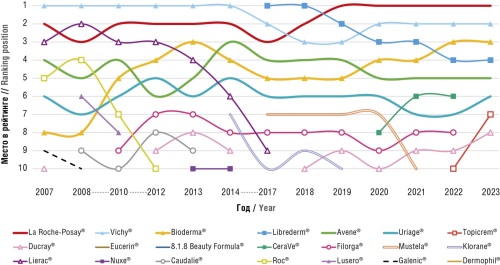
Objective: To analyze competition and the level of dominance in the cosmetics sector within pharmacy sales, identifying trends in three key segments: selective, mass-market, and active (therapeutic) cosmetics.
Material and methods. The study was based on annual reports on the Russian pharmaceutical market published by DSM Group. The analysis employed the Linda index and the Herfindahl–Hirschman Index (HHI), as well as the strength/variety (SV) matrix, which includes concentration ratios and the modified Hall–Tideman index. The degree of market concentration was assessed, the presence of dominant groups was identified, and the market structure and dynamics of major players’ rankings were analyzed.
Results. The Russian cosmetics market within pharmacy sales demonstrates both similarities and significant differences across segments. In the selective cosmetics segment, where foreign players dominate (with the exception of the domestic brand Librederm®), a transformation has occurred – from high brand differentiation to a state close to a natural oligopoly. This trend has been accompanied by the strengthening of positions of Russian brands since 2014. In contrast, the mass-market cosmetics segment, characterized by high dynamism and competition, shows low market concentration and more diffuse leadership. The ambiguous dynamics of international players after 2014 have been accompanied by the strengthening of domestic brands such as Moe Solnyshko®, which indicates the effect of geopolitics not only on the selective cosmetics segment, but also on mass-market cosmetics. The active (therapeutic) cosmetics, where Russian manufacturers are market leaders, show relative stability of individual brands, such as Alerana®, against a backdrop of high market variability. The absence of a dominant group confirms the high level of competition.
Conclusion. There are differences in the development of cosmetic segments within pharmacy sales; the selective cosmetics segment is the most concentrated, in contrast to the mass-market and active (therapeutic) cosmetics segments, which are characterized by a high level of competition. The significance of domestic brands has increased following the introduction of sanctions.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used for effective pharmacotherapy of inflammation and pain, but long-term NSAID therapy and/or their inappropriate use can lead to damage to the gastrointestinal tract
► Diclofenac with zinc complex exhibits the same anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects, but cause a lower incidence of gastric lesions compared to diclofenac
► The combination of zinc and NSAIDs is a donor of the essential trace element zinc, which exhibits anti-inflammatory, wound healing and immunomodulatory qualities
What are the new findings?
► Chemoreactomic analysis showed that zinc-containing compound pilim-1 (bis-(1-vinylimidazole) zinc diacetate) is a promising molecule with anti-inflammatory activity, devoid of ulcerogenic effect
► The anti-inflammatory effect of pilim-1 is realized through the modulation of cytokine activity, prostaglandin and leukotriene metabolism; the analgesic effect is based on the inhibition of kinin and histamine receptors
► Pilim-1 is neutral in relation to vitamin metabolism, while being comparable in strength of anti-inflammatory action with zinc-containing derivatives of NSAIDs
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Based on pilim-1, the creation of a drug with pronounced anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties that does not have ulcerogenic effect is promising
► With a daily requirement for zinc of about 15–20 mg, рilim-1 and the studied zinc-NSAIDs are significant sources of elemental zinc
Background. Gastroenterological side effects (esophageal, gastric, and intestinal erosions) associated with the use of drugs from the group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) highlight the need to explore new molecule candidates with reduced ulcerogenic effects. The zinc-containing molecule candidate pilim-1 has the potential to exhibit anti-inflammatory effects and improve the regenerative properties of the gastric mucosa.
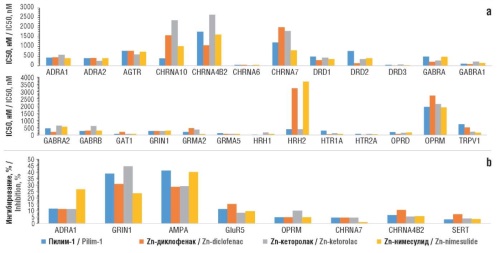
Objective: To explore the anti-inflammatory, ulcerogenic, analgesic, and antivitamin effects of the pilim-1 molecule using chemoreactomic methods.
Material and methods. The chemoreactomic assessment of the pharmacological properties of pilim-1 and zinc derivatives of well-known NSAIDs (ketorolac, diclofenac, and nimesulide) was carried out using the methods of chemoinformatic analysis of molecules developed within the scientific school of Academician Yu.I. Zhuravlev.
Results. Pilim-1 exhibits a distinct anti-inflammatory effect realized through modulation of cytokine activity as well as prostaglandin and leukotriene metabolism. A key distinguishing feature of the pilim-1 molecule is its neutrality with respect to vitamin metabolism while demonstrating a comparable anti-inflammatory potency to zinc-containing NSAID derivatives. The analgesic effect of pilim-1 is based on the inhibition of kinin and histamine receptors. The nociceptin receptor ORL1 can be inhibited by pilim-1 more effectively (IC50 198–214 nM) than zinc-NSAIDs (IC50 361–1093 nM). In the phenylquinone-induced writhing test in rats, pilim-1 demonstrated a slightly higher percentage of analgesia (44%; zinc-NSAIDs: 21–43%). The incidence of gastric ulcers at an oral dose of 100 mg/kg was estimated at 35% (compared to 75% with other molecules). Compared to other zinc-derived NSAID derivatives, pilim-1 exhibits minimal impact on vitamin and mineral metabolism.
Conclusion. Chemoreactomic analysis of pilim-1 indicates promising prospects for its application as an anti-inflammatory drug.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Since 2014, there has been a global increase in the number of artificial intelligence (AI) smartphone applications for the early detection of malignant skin tumors (MSTs)
► There is a high turnover of such AI programs for smartphones due to their insufficient diagnostic accuracy
► In Russia, AI-based smartphone applications for diagnosing skin tumors are insufficiently represented, and data on their diagnostic and clinical accuracy are limited or absent
What are the new findings?
► The Derma Onko Check AI smartphone application can be used in primary health care for the differential diagnosis of benign skin tumors (BSTs) and MSTs by general practitioners and specialists without sufficient specialized knowledge in dermatovenerology and oncology
► The Derma Onko Check program is an effective tool for the differential diagnosis between BSTs and MSTs of various tissue origins, demonstrating high diagnostic accuracy (96%), sensitivity (98%), and specificity (96%)
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► General practitioners and other specialists using AI-based software applications (for smartphones) can reliably perform differential diagnosis between BSTs and MSTs. This will improve the quality of early detection of MSTs and expedite referral of such patients to oncologists
Objective: to evaluate the effectiveness of preliminary differential diagnostics of benign and malignant skin tumors during initial medical consultations in primary health care using the Derma Onko Check artificial intelligence (AI) program for electronic computing devices (smartphone application).
Material and methods. The effectiveness of the Derma Onko Check program for visual identification of benign and malignant skin tumors was evaluated in 135 patients aged 22 to 78 years with various skin lesions that appeared visually suspicious for malignancy. The conclusions generated by the program were compared with the results of dermatoscopic and morphological examinations.
Results. The diagnostic accuracy of the Derma Onko Check program in determining the likelihood of a patient having a benign or malignant skin tumor was 96%, sensitivity was 98%, specificity was 96%, the proportion of false-positive results was 4.3%, and the propor
Conclusion. The use of modern AI-based software for electronic computing devices enables early detection of malignant skin tumors during initial examinations in primary health care. This is particularly relevant for medical institutions and regions with a shortage or absence of dermatologists and oncologists.
tion of falsenegative results was 2.4%.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Bioimpedance is a marker of morphological constitution, a kind of “mirror” for metabolic processes in the body under various pathologies
► Bioimpedance assessment in clinical practice is aimed at early correction of adverse changes in body composition
► Excess adipose tissue, especially visceral fat, loss of muscle mass, negative changes in fluid balance, and reduced bone density are characteristic of kidney diseases
What are the new findings?
► Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) are characterized by older age, excess body weight (as confirmed by bioimpedance and biochemical blood tests), higher blood pressure, and multiple organ pathology
► The indicator “lean mass, kg” increases monotonically with height, body weight, waist circumference, intracellular fluid, basal metabolic rate, and total body water and, conversely, decreases monotonically with increasing active resistance 5 and 50 kHz as well as reactive resistance 50 kHz
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► It is promising to further investigate the informativeness and predictive strength of CKD predictors
► It is important to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the effectiveness of various therapies for renal pathology in subgroups of CKD patients with different disease severity, taking into account their impact on impedance parameters
► It is necessary to assess the efficacy of various therapeutic approaches, the role of physical activity and micronutrient status (if relevant data are available)
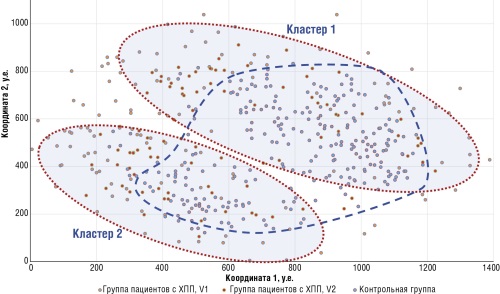
Objective: To identify potential predictors of chronic kidney disease (CKD) based on the analysis of interrelationships between somatometric (including bioimpedance), biochemical, and clinical indicators in CKD patients.
Material and methods. The values of 58 indicators describing the condition of 357 participants were collected: 128 patients with CKD and 229 participants in the control group (without kidney pathology). Demographic, anthropometric, anamnestic data (19 diagnoses according to the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision), bioimpedance values, results of general and biochemical blood tests (19 indicators), and diet indicators (using the CINDI survey) were studied. New mathematical approaches were applied to establish informative value intervals for numerical indicators, to find metric clusters in the multidimensional space of biomedical indicators, and to construct metric maps.
Results. In the CKD group, a predominance of older patients (mean age 54.1±13.1 years) as well as overweight people (82.18±19 kg) was observed compared to the control group (48.78±9.75 years and 74.7±17.45 kg, respectively). Patients with CKD exhibit disturbances in adipose tissue metabolism, decreased active and reactive bioimpedance resistance, high systolic blood pressure, and multiple organ pathology.
Conclusion. The analysis of the cluster of interrelationships between indicators made it possible to outline promising areas for further research. These include a more detailed investigation of informativeness and predictive strength of CKD predictors, a comprehensive assessment of treatment effectiveness, identification of differences between subgroups of patients with different nosologies and stages of CKD, evaluation of the efficacy of various therapeutic approaches, the role of physical activity, and micronutrient status.
REVIEW ARTICLES
What is already known about thе subject?
► Genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) is a term proposed to describe a range of genital and urinary symptoms that may occur during and after menopause. In addition, GSM symptoms can occur earlier due to cancer therapy or after bilateral oophorectomy
► Symptoms of VVA are common and include vaginal dryness or vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA), discomfort and dyspareunia, burning and itching, and urinary frequency urgency
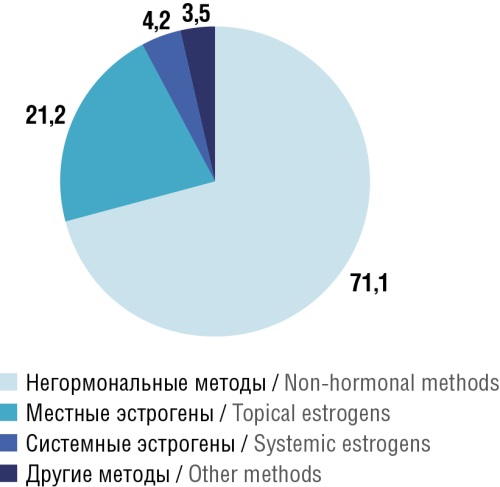
► First-line treatment consists of non-hormonal methods (lubricants/moisturizers). The “gold standard” is vaginal estrogen therapy at the lowest effective dose, but there are several concerns about estrogen therapy, ranging from the inconvenience of vaginal insertion to neoplasm developing
What are the new findings?
► Although hormonal therapy is the “gold standard” of treatment for GSM, it is generally ineffective in VVA. This is partly because hormonal therapy provides only a symptomatic effect; as a result, once hormone administration is stopped, the involution process resumes
► Selective estrogen receptor modulators such as lasofoxifene and ospemifene, as well as the addition of lactobacilli, vitamins D and E to the treatment regimen, demonstrate beneficial effects on vaginal tissue in women with VVA symptoms
► Vaginal dehydroepiandrostenedione, vaginal testosterone, and tissue-selective estrogen complexes are emerging as promising new treatments. New therapeutic approaches using laser therapy and injection procedures into the periurethral area and vaginal walls may be used as alternative options
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Use of injectable materials (autologous platelet-rich plasma, hyaluronic acid (HA), non-cross-linked HA plus calcium hydroxyapatite, micro-fragmented adipose tissue, hybrid hyaluronan cooperative complexes, сross-linked HA, microfat and nanofat transplantation) are effective methods in the treatment of GSM
► In women with a history of cancer, new treatments (laser therapy, vaginal injections) show promising results with minimal side effects and hormone-independent mechanisms. Treatment should be individualized based on the risk-benefit ratio for each рatient
► In some cases (in hormone-independent breast cancer or in hormone-dependent tumors, after completion of antihormonal adjuvant therapy), the use of vaginal estrogens can be considered, which should be administered topically, in a minimal dose and for a limited period until symptoms improve
Background. Treatment of vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) in women diagnosed with gynecologic or breast cancer presents challenges. Treatment options for VVA, the genital manifestation of the genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM), generally mirror those used for natural menopause; however, efficacy and safety data specific to this patient group are limited due to their exclusion from clinical trials.
Objective: To review the literary data on new approaches to the treatment of VVA as a manifestation of GSM in women with gynecological or breast cancer.
Material and methods. The search in PubMed/MEDLINE, Web of Science, Google Scholar, eLibrary, and Scopus databases was performed using the following key phrases: “vulvovaginal atrophy”, “vulvar atrophy after cancer”, “treatment of vulvar atrophy in women with cancer”, “low dose estrogen therapy”, “laser therapy of vulvovaginal atrophy”, “vulvovaginal atrophy following treatment for oncogynecologic pathologies”, “genitourinary syndrome of menopause in breast cancer survivors”, “low dose estrogen therapy”, “laser therapy of vulvovaginal atrophy” in Russian and English. We also reviewed important sources cited in the bibliographies of relevant studies. The review included original and review articles containing the mentioned key phrases and published from 1996 to March 2025.
Results. In women with a history of gynecological or breast cancer, treatment of VVA should be tailored to the individual, and non-hormonal options such as lubricants during sexual activity and regular use of long-lasting vaginal moisturizers are typically the first line of treatment. Fractional CO2 laser therapy is an effective and safe method for gynecological cancer survivors, enhancing sexual life and overall quality of life. In this patient population, hyaluronic acid combined with vitamins A and E has demonstrated a beneficial effect, reducing vaginal dryness and dyspareunia. The use of topical hormonal therapy may be an option for women who do not respond to non-pharmacologic and nonhormonal treatments after discussing the risks and benefits and consulting with an oncologist.
Conclusion. Not all available treatment options are suitable for women with a history of cancer due to the risk of recurrence of hormonedependent cancer associated with estrogen therapy. In this patient population, new treatments such as laser therapy and vaginal injections show promising results with minimal side effects and hormone-independent mechanisms.
What is already known about thе subject?
► IgA nephropathy (IgAN) is characterized by a heterogeneous risk of progression that depends on multiple factors. Although numerous studies have been conducted, universal treatment approaches that take IgAN progression risk into account have not yet been developed
► A high risk of IgAN progression is defined as persistent proteinuria (>1 g/day) regardless of optimal supportive therapy for at least 3 months
What are the new findings?
► It has been established that the most significant predictors of IgAN progression are proteinuria and arterial hypertension, taking into account baseline kidney function
► Analysis of histological changes in specific structures within the kidney biopsy area according to the MEST-C classification, combined with clinical data, improves the accuracy of individual risk assessment for IgAN progression
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The development of a tool for assessing the individual risk of IgAN progression, taking into account clinical, and histological data as well as other predictor biomarkers, will make it possible to determine the changing risk for a particular patient at different stages of the disease
► The establishment of a universally accepted risk stratification system for IgAN progression will help optimize and personalize the treatment at early stages of the disease and improve the long-term prognosis
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy is the most common form of chronic glomerulonephritis and one of the leading causes of end-stage renal disease. Currently, the ability to accurately predict the risk of this progression at the individual patient level is limited. This paper analyzes the scientific literature containing research results focused on identifying independent predictors of IgA nephropathy progression risk. According to most studies, variables such as proteinuria, arterial hypertension, and baseline kidney function have a stable and independent association with worse kidney prognosis. Histological changes in kidney biopsy serve as independent predictors. The combination of morphologic and clinical data improves predictive accuracy. To enhance treatment outcomes and long-term prognosis, further research is necessary, including the search for new biomarkers and the development of a universally accepted risk stratification system.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
ISSN 2070-4933 (Online)