ORIGINAL ARTICLES
What is already known about thе subject?
► Chronic hepatitis C (CHC) is among the diseases of high medical and social significance in Russia
► The elimination of CHC in the country will require years of systematic work and significant financial investment
► The Russian healthcare system is currently actively establishing a systematic approach to CHC control
What are the new findings?
► A functional model of the medical care system for CHC in Russia was developed, which made it possible to estimate approximate costs and expected outcomes
► Recommendations were proposed to improve the system of medical care for CHC patients
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The results can be used in planning financial support for measures to combat CHC at both federal and regional levels
► The data obtained will help in selecting and planning drug provision at the regional level and for medical institutions
► The proposed measures to improve the efficiency of CHC control activities can be considered a priority for implementation at the federal and regional levels
Objective: To explore approaches to improving medical care for patients with chronic hepatitis С (CHC) at the national level.
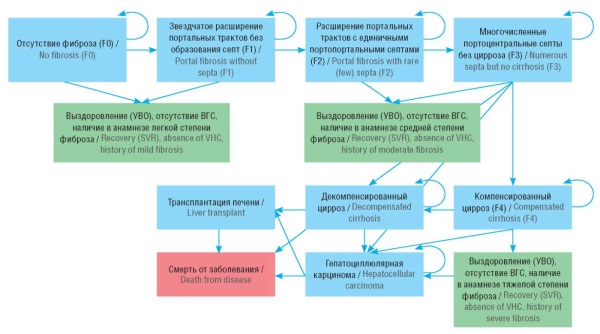
Material and methods. A Markov model was used to predict the direct medical costs and outcomes (e.g., number of cured and died patients, cases of complications) for the treatment of CHC for 6 years in 300,000 patients. Two modeling scenarios were considered: a basic scenario included therapy administered with drugs in accordance with clinical guidelines and the standard of medical care for CHC patients; an alternative scenario focused on therapy with pan-genotypic drugs only.
Results. In the basic scenario, 298,034 people, or 99.3% of the cohort are treated over a period of 6 years. During this time, the disease develops into 236 cases of decompensated liver cirrhosis, 2,073 cases of hepatocellular carcinoma, 62 liver transplants required, and 430 deaths from complications of progressive liver decompensation. Total direct medical costs for this period are estimated at 105.3 billion rubles. Annual costs range from 16.5 billion rubles in the first year to 18.2 billion rubles in the sixth year. In the alternative scenario, a slight improvement in clinical outcomes is observed; however, the treatment cost increases from 105.8 billion rubles to 114.5 billion rubles (+8.7 billion rubles). It was found that decrease in the cost of drugs by 10%, 20%, 30%, or 40% can provide additional treatment for 31,706, 70,907, 120,615, and 185,707 patients, respectively.
Conclusion. The study made possible to assess the efficiency of the proposed measures for treating patients with CHC over a 6-year horizon, as well as the financial requirements for their implementation. Furthermore, possible measures to improve the effectiveness of CHC control activities and prospective ways to realize the benefits that could be achieved by reducing the cost of drug therapy were considered.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Anxiety disorders are among the most common psychiatric disorders
► Current therapeutic strategies are based on the use of antidepressants, mainly selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
► Along with benzadiazepines, whose consumption is decreasing worldwide due to potential adverse reactions, other anxiolytics are increasingly used to treat anxiety disorders. These are buspirone, etifoxine, hydroxyzine and fabomotizol, as well as antipsychotics. The actual practice of pharmacotherapy for anxiety disorders in Russia remains unknown
What are the new findings?
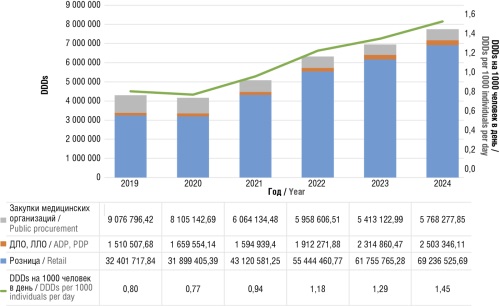
► In 2019–2024, the sales of anxiolytics almost doubled: from 43 million defined daily doses (DDDs) in 2019 to 77.5 million DDDs in 2024. Up to 90% of sales are in the retail segment, i.e. the costs of their purchase are not reimbursed by the healthcare system
► A twofold decrease in the consumption of benzodiazepines was noted, with a threefold increase in the sales of hydroxyzine and a twofold increase in the sales of buspirone
► The sales of bromodihydrochlorophenylbenzodiazepine (e.g., phenazepam) decreased by 2.7 times during the study period: from 806 million rubles in 2019 to 292 million rubles in 2024
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The distribution of the practice of prescribing non-benzodiazepine anxiolytics requires careful collection of data on the safety of their use
Objective: To assess the structure and volume of anxiolytic consumption in the Russian Federation in 2019–2024.
Material and methods. Data on sales of medicines belonging to the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification class N05B (anxiolytics) contained in the IQVIA database and selected to treat patients with neurotic stress-related and somatoform disorders according to the current Russian clinical guidelines were derived. The study period of 2019–2024 covered such drugs as diazepam, alprazolam, lorazepam, bromdihydrochlorophenylbenzodiazepine, tofizopam, fabomotizole, etifoxine, buspirone, and hydroxyzine. Consumption was assessed at defined daily doses (DDDs) in each year of observation. The number of DDDs per 1000 individuals per day was calculated. For drugs without specified DDDs, consumption was calculated based on the absolute value sold in rubles in each year of the study.
Results. During the 2019–2024 period, an almost twofold increase in the sales of anxiolytics was noted: from 43 million DDDs in 2019 to 77.5 million DDDs in 2024. This increase was primarily attributed to a 2.5-fold increase in the sales of hydroxyzine (to 44.1 million DDDs in 2024) and a twofold increase in the sales of buspirone (to 2.3 million in 2024). The estimated consumption per 1000 individuals per day increased from 0.8 DDDs in 2019 to 1.45 DDDs in 2024. The sales of benzodiazepines decreased from 24.4% in 2019 to 10.9% in 2024. Among the anxiolytics without specified DDDs, fabomotizol ranked first in terms of acquisition costs, amounting to 2.1 billion rubles in 2019 and 3.2 billion rubles in 2024. The sales of bromodihydrochlorophenylbenzodiazepine decreased 2.7 times during the study period: from 806 million rubles in 2019 to 292 million rubles in 2024.
Conclusions. Due to the reduction in benzodiazepines consumption, the risks of prescribing other classes of psychotropic drugs, such as antipsychotics including off-label indications, are high. This requires careful monitoring of adverse drug reactions, including those associated with low compliance.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Reference materials (RMs) are essential for drug quality control. They are used for instrument calibration, method validation, and ensure traceable measurements at all stages of pharmaceutical quality assurance
► RMs must meet strict requirements for purity, stability, and homogeneity, since the accuracy of analytical results and the safety of medications directly depend on the reliability of these standards
► Production of RMs is governed by the international and national standards, as well as guidelines for good practices that define quality management requirements for reference standard production
What are the new findings?
► It was demonstrated that integrating international quality standards and good practice requirements in RM production covers all quality aspects, from documentation to sample stability
► Comparison of Russian and foreign practices showed convergence: Russia is introducing accreditation and international cooperation in RM production, and ultimately all producers strive to meet the same international quality criteria
► Key challenges in implementing a quality management system (QMS) were highlighted: resource constraints, complex multi-level requirements, and technical issues of RM stability. Future steps were proposed: harmonizing standards, digitizing processes, and expanding the range of RMs for new drugs
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► A robust QMS for RM production ensures accurate drug quality control. As a result, only safe and effective medications reach clinical practice, improving treatment safety and patient trust
► Harmonizing international quality requirements for RMs and digitalizing quality control processes will improve the reliability of laboratory tests. This will lead to better diagnostics, improved treatment monitoring, and enhanced patient outcomes
► International mutual recognition of certified RMs will accelerate drug registration and market launch of innovative medicines, increasing patient access to cutting edge therapies
Objective: To summarize current requirements for the quality management system (QMS) in the production of reference materials (RMs) for pharmaceutical and medical applications, as well as to assess the challenges and prospects of system implementation to ensure reliable quality control of medicinal products.
Material and methods. The study analyzed international and national regulatory documents, including ISO 9001, ISO/IEC 17025, ISO 17034 standards as well as good manufacturing practice (GMP) and good laboratory practice (GLP) guidelines. Experiences in QMS implementation at RMs manufacturing enterprises in Russia and abroad was examined. The research methodology was based on a comparative analysis of requirements and practical approaches to quality assurance.
Results. Ensuring RM production quality requires integration of the international standards ISO 9001, ISO/IEC 17025, ISO 17034, and GMP/GLP guidelines. Comparative analysis showed that the Russian quality system in RM production is gradually aligning with the global benchmarks through ISO-based accreditation and international cooperation, while retaining elements of state regulation. Promising directions for QMS development include further harmonization of international standards, digitalization of quality control, and differentiation of RMs to include new medicinal product types. All this necessitates development of novel methodology.
Conclusion. An effective QMS in RM production is a critical factor in ensuring the quality and safety of pharmaceutical products. Integration of ISO standards and GMP/GLP principles enables the production of reference materials with the required accuracy, stability, and traceability, recognized at the international level. Further improvement of the quality system will provide the industry with reliable reference materials and enhance confidence in quality control results both domestically and internationally.
What is already known about thе subject?
► The analysis of the FAERS database, which contains reports of adverse drug reactions in individual patients, revealed a high rate of complications associated with use of the majority of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
► The safety of NSAIDs should be assessed based on their interaction not only with cyclooxygenases 1 and 2, but also with other proteins of the proteome
What are the new findings?
► The methods of chemoinformatic analysis of molecules allows the spectra of the pharmacological action of drugs to be evaluated, determining differences in the molecular-pharmacological mechanisms of action of NSAIDs and other drugs
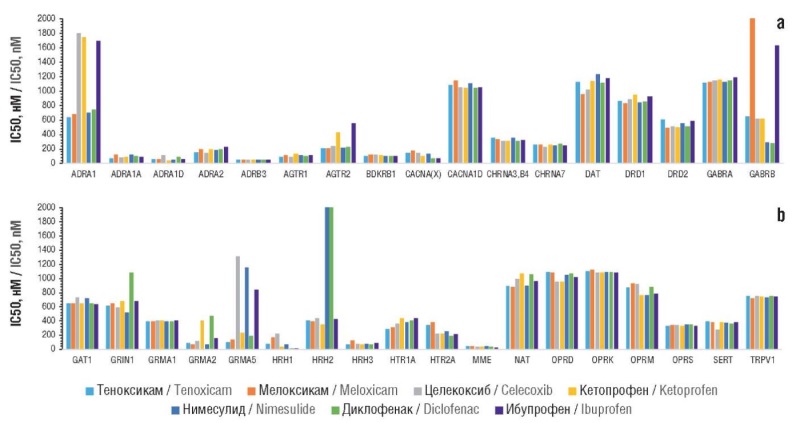
► Tenoxicam, unlike other molecules, can have a significant effect on the synthesis, secretion and activity of leukotriene B4 and exhibit inhibitory effects on kinin receptors. It does not stimulate greater micronutrient losses than other NSAIDs
► The analysis of the frequency of various side effects, averaged over their studied sample, revealed that tenoxicam was characterized by the lowest indicator
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The chemoreactomic, chemoproteomic and pharmacoinformatic profiling of tenoxicam indicated its enhanced efficacy-safety balance compared to reference molecules
Background. Organization of effective and safe pharmacotherapy for pain and inflammation requires knowledge of the mechanisms and spectrum of action of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These concern their anti-inflammatory, analgesic (including central) effects, effects on the proteome, micronutrient metabolism and other aspects of the body's metabolism depending on the administration route.
Objective: To compare the effects of tenoxicam, meloxicam, celecoxib, ketoprofen, nimesulide, diclofenac, ibuprofen molecules using the methods of chemoreactomic, chemoproteomic and pharmacoinformatic analysis.
Material and methods. The comparison of tenoxicam with other NSAIDs was conducted using the methods of topological analysis of Yu.I. Zhuravlev and K.V. Rudakov scientific school. These methods were developed based on the combinatorial theory of solvability and the classification theory of feature values as applied to chemographs, i.e. mathematical structures describing the chemical structures of molecules.
Results. In silico estimates of anti-inflammatory, central, and analgesic effects of tenoxicam and comparison molecules were obtained. The profiles of belonging to various anatomical-therapeutic-chemical classification groups and the profiles of side effect frequencies of the NSAIDs (including the effect on micronutrient metabolism through the loss of vitamins and microelements) were analyzed. A comparison of the effects of molecules under oral, topical and parenteral administration was carried out. The profile of the pharmacological effects of tenoxicam differed significantly from those of other NSAIDs, indicating, in particular, potential antithrombotic, hypoglycemic, and antihistamine effects. Tenoxicam, unlike other molecules, exhibits a significant effect on the synthesis, secretion and activity of leukotriene B4 along with inhibitory effects on kinin receptors. In comparison with other NSAIDs, tenoxicam does not stimulate stronger losses of micronutrients. Chemoreactome assessments of the central effects of tenoxicam showed its comparability with other NSAIDs. The effects of tenoxicam under its topical, oral and parenteral administration are comparable to the anti-inflammatory action of other NSAIDs. The frequency analysis of various side effects, averaged over the studied sample of side effects, showed that tenoxicam was characterized by the lowest frequency of all the indicated side effects (3%; other molecules: 4–7%).
Conclusion. The chemoreactomic, chemoproteomic and pharmacoinformatic profiling of tenoxicam indicated its improved efficacy-safety balance compared to other NSAIDs.
What is already known about thе subject?
► In Russia, health technology assessment specialists consider it essential to incorporate real-world evidence (RWE) analysis into comprehensive drug assessment
► Expert-based recommendations suggest incorporating RWE into the comprehensive drug assessment when it includes the analysis of additional consequences
What are the new findings?
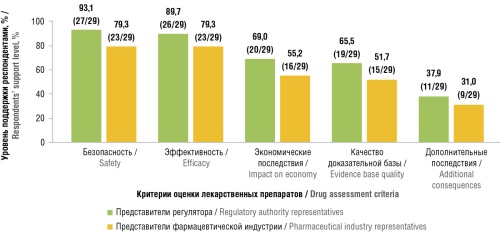
► Our survey demonstrated that RWE-based evaluation received support from both regulators and pharmaceutical industry representatives
► According to expert opinion, RWE analysis is relevant in evaluating criteria such as safety, efficacy, impact on economy, and the quality of evidence supporting a pharmaceutical product
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The obtained data indicate the promising potential of incorporating RWE analysis into the comprehensive drug assessment
► The results justify the development of RWE assessment methods using a specific set of criteria
Background. Specialists in health technology assessment consider real-world evidence (RWE) a promising path for improving comprehensive drug assessment (CDA). Therefore, it is particularly important to elicit opinions from CDA experts on the necessity of incorporating RWE analysis into the assessment process.
Objective: To present the results of a survey of CDA specialists demonstrating their views on the necessity and variability of incorporating RWE into the CDA process.
Material and methods. The survey was conducted in the form of a specially developed original questionnaire between July 2024 and February 2025 among two groups: regulatory authority representatives and pharmaceutical industry representatives involved in CDA.
Results. The survey involved 29 representatives from both regulatory authorities and pharmaceutical industry. The majority of respondents support the inclusion of RWE in CDA: 96.6% of regulatory authority representatives vs 75.9% of industry representatives. The most favored assessment areas using RWE were safety, efficacy, impact on economy, and the quality of evidence base for medicinal products. The predominant view was that in decision-making, the role of RWE should be informative rather than restrictive.
Conclusion. The surveyed respondents specialising in CDA predominantly hold positive attitudes towards incorporating RWE into the assessment procedure. The support of this incorporation by experts implies that work on specific implementations of RWE in CDA is fully justified and promises to be successful.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Сonvolutional neural networks (CNNs) are widely used in medical diagnostics; however, these architectures have limitations in interpretability and robustness to domain shifts
► Vision transformers (ViT) demonstrate high performance in image classification tasks
► Class balancing and data augmentation are critical for model quality
What are the new findings?
► This study is one of the first to directly compare CNN and ViT architectures in the task of skin tumor classification using clinically relevant metrics
► ViT showed superiority in accuracy (up to 92.93%) and specificity (up to 95%), particularly in complex diagnostic cases
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► ViT implementation will improve the accuracy of melanoma diagnostics and reduce the number of false positive results
► Hybrid solutions (CNN + ViT) can become the standard for automated differential diagnosis of benign and malignant skin lesions, melanoma in particular
► The results highlight the importance of data quality and pre-processing methods for implementing artificial intelligence in medicine
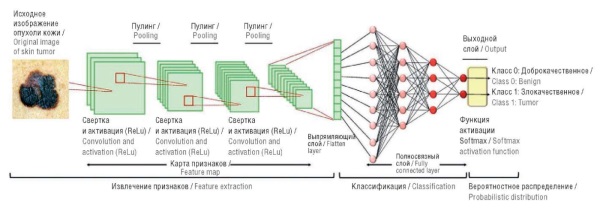
Background. When applying computer vision programs in artificial intelligence (AI) models to diagnose skin tumors, melanoma in particular, even minimal classification errors are critical. Vision transformers (ViT), a new model architecture, have shown promising results in computer vision; however, their efficiency in classifying skin lesions has received insufficient research attention. This study is one of the first to directly compare convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and ViT on clinically relevant metrics, which is especially important for the implementation of AI in dermatological and oncological practice.
Objective: To compare the performance of CNNs and ViT in the tasks of binary classification of skin lesions: “melanoma/not melanoma” and “benign/malignant”.
Material and methods. The study used CNN (MobileNetV2, Xception) and ViT architectures. Testing was carried out on independent datasets (3000 and 4800 images, respectively) with assessment by the metrics of accuracy, sensitivity, specificity. Augmentation, class balancing, hyperparameter optimization, and data cleaning from artifacts were used.
Results. ViT showed superiority over CNNs. Thus, in the “melanoma/non-melanoma” task, the accuracy was 92.93% versus 88% for Xception, and in the “benign/malignant” task – 91.35% versus 85%. Transformer model demonstrated better specificity (up to 95%).
Conclusion. ViT provides higher accuracy due to the analysis of global patterns, although requiring careful tuning and high-quality data. CNNs remain a stable solution with limited data. For clinical use, a combination of both architectures is recommended to improve the reliability of diagnostics.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Phenol and its derivatives (parabens), phthalates, and benzene tars exhibit a variety of toxic effects, entering the human body due to unfavorable ecology, smoking, intake with food and medications
► A systematic assessment of clinical consequences of toxic exposure to phenol and phthalates in comprehensive clinical and epidemiological studies has not previously been conducted
What are the new findings?
► Higher urine phenol levels are associated with increased levels of bone and cartilage destruction markers, hematopoiesis disorders, liver and kidney dysfunction, and decreased systolic blood pressure, in the setting of lower intakes of fiber, vitamins E, A, C, B2, B6, folates, and magnesium
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Intake of vitamin and mineral supplements is an effective measure of micronutrient support for the body's detoxification systems against the action of phenol and its derivatives
Background. Phenol and its derivatives (eg. parabens), phthalates and a number of other aromatic compounds exhibit various toxic effects when entering the human body due to unfavorable ecology, smoking, intake with food and medications. Integrated clinical and epidemiological studies into the clinical consequences of such effects are currently lacking.
Objective: To identify patient history parameters that are significantly associated with blood and urine levels of phenols and urine levels of phthalates.
Material and methods. The database of the UNESCO Institute for Microelements was used to compile a sample of patient descriptions (n=2746) containing information on the serum and/or urine levels of phenol and urine levels of phthalates. The data sample was analyzed using the methods of Zhuravlev–Rudakov topological and metric data analysis, as well as parametric and nonparametric statistics. The data analysis was carried out in three stages: (1) identification of statistically significant pairwise interactions by the methods of topological data analysis; (2) identification of clusters of pairwise interactions; (3) description of the obtained patterns in the form of metric diagrams, topological “interaction formulas” and “interaction types”.
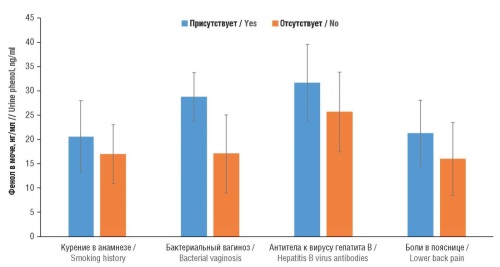
Results. Higher urine levels of phenol were associated with increased levels of bone and cartilage destruction markers, hematopoiesis disorders (decreased hemoglobin and mean corpuscular volume), liver and kidney dysfunction (increased creatinine and albumin levels), decreased systolic blood pressure (hypotension) in the setting of lower intake of fiber, vitamins E, A, C, B2, B6, folates, and magnesium. Higher urine phenol concentrations were correlated with higher levels of a smoking biomarker (cotinine), indicating that smoking is a significant source of phenol and its derivatives in the human body. Higher blood phenol concentrations were associated with a history of smoking, asthma, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), vasomotor paroxysms (hot flashes), and pain symptoms. Significantly higher blood phenol concentrations were found in participants not taking vitamin and mineral supplements (VMS). Higher urine phthalate levels were found in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), alcoholism, pain symptoms (headaches, lower back and leg pain), diabetic polyneuropathy, hematopoiesis disorders (increased erythrocyte distribution width), cartilage homeostasis, liver dysfunction, kidney dysfunction and, in general, a decreased quality of life. Elevated urine phthalate levels corresponded to a lower intake of vitamins A, C, B2, B12, folates, cobalt, iron and lutein n the setting of higher blood concentrations of toxic cadmium, lead and cotinine. This confirms the correlation between smoking and increased concentrations of phenol and its derivatives.
Conclusion. Elevated urine levels of phenols and phthalates and blood serum levels of phenols are associated with a number of socially significant chronic pathologies (T2DM, COPD, pain, cartilage, and bone homeostasis disorders) and with lower VMS intakes. Thus, correction of the vitamin and microelement status is an ffective approach to supporting the body's detoxification systems against the negative impact of phenol and its derivatives.
What is already known about thе subject?
► The most common criteria for the selection of a pharmaceutical organization are the convenience of its location, the price and assortment of goods. Lack of personnel in the pharmaceutical industry is predicted
► Under the current conditions of digitalization, the Internet is one of the most used sources of medical and pharmaceutical information for both specialists and patients
► In addition to specialized sources of medical and pharmaceutical information, patients, including for self-medication, can use various Internet websites, platforms and social networks, which may supply unreliable data
What are the new findings?
► The most common objects of pharmaceutical information search are the desired drug and the assortment of goods. Internet ordering is a service in demand. Information search correlates with high self-medication rate
► Patients often violate the recommendations of pharmaceutical specialists; many pharmacy visitors doubt their qualifications. High patient compliance correlates with low self-medication rate
► Negative information about a pharmacy can cause a refusal to visit it or a decrease in trust in the specialist – and, accordingly, compliance. A positive attitude toward pharmaceutical specialists is a predictor of a low tendency to self-medication
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► It is necessary to regularly monitor the content of pharmaceutical information on the Internet
► Data on the correlation of self-medication with age and sex can be used to create personalized recommendations, social campaigns, governmental programs, and advertising
► To reduce the incidence of self-medication and increase compliance, it is important to contribute to forming a positive image and attitude toward pharmaceutical specialists among the population
Objective: An analysis of pharmaceutical information as a factor in self-medication and the loyalty of pharmacy visitors.
Material and methods. Sociological survey was conducted with 2888 respondents, poll`s period February – March 2025 inclusive. The geographical coverage included 58 subjects of the Russian Federation. The questionnaire consisted of questions to identify the respondent's characteristics (gender, age, region of residence), frequency of self-medication, attitude of pharmacy visitors to pharmaceutical specialists and their recommendations. Kendall's and Spearman's rank correlation coefficients were used when processing the questionnaires.
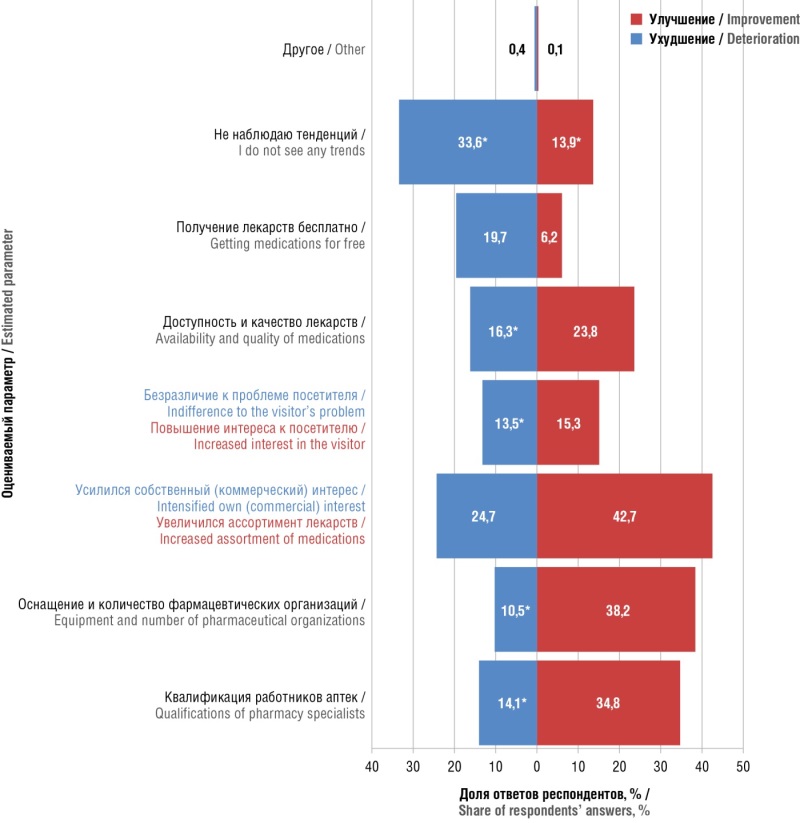
Results. 88,3% of respondents use self-medication, and 42,8% do it often and constantly. Factors that increase the tendency toward self-medication are the female sex and young age. There is no correlation between the high frequency of self-medication and visits to pharmacy organizations. The main criteria for choosing a pharmacy organization are the price of the desired product, proximity to home/work, and the range of products offered. Most often, respondents are interested in the drug as well as the assortment of goods. Internet ordering is also popular. Searching for information on the Internet about a drug, assortment, pharmacy, or online order correlates with more frequent self-treatment. Respondents indicated time and/or cash savings as the main reasons for searching for information. Only 37,1% of respondents always fully follow the recommendations of pharmacy workers, and patient compliance naturally negatively correlates with self-medication. 20,6% of respondents indicated distrust of the qualifications of a pharmacy specialist and/or considered, that their recommendations optional. Reluctance to change lifestyles, as well as a lack of belief in the outcome, correlated with male gender and younger age. Among the positive trends in pharmacies, the most often noted were an increase in the range of drugs, an improvement in equipment, and the number of organizations. Among the negative trends in the pharmaceutical industry, respondents noted an increase in self-interest (commercial interest) among pharmacy workers – 24,7% of respondents answered so. Only 38,4% of respondents noted the possibility of error or subjectivity in someone else's negative opinion about the pharmacy. A more positive attitude toward the pharmacy worker generally correlated with a lower frequency of self-medication.
Conclusion. The results of the sociological study demonstrate the importance of pharmaceutical information and attitudes toward pharmacy workers as factors in self-medication. The data obtained can serve as the basis for targeted advertising, considering age and gender preferences, and popularizing the appeal to a specialist. It is also necessary to monitor and update information freely available on the Internet.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Homeopathic medicines (HMs) are used as part of integrative medicine, being in steady demand in different countries. In recent years, there has been a growing global interest in natural-origin remedies due to their more gentle therapeutic effects
► HMs have existed in the pharmaceutical market of Azerbaijan since the late 20th century, however, no dynamic reviews or statistical analyses have previously been conducted
► The pharmaceutical market of Azerbaijan shows a growing interest in integrative and complementary medicine, with diverse foreign suppliers. The development of medicines based on local natural resources is of interest
What are the new findings?
► It was shown that the pharmaceutical market of Azerbaijan offers a relatively wide range of HMs. A quantitative and structural analysis of its breadth, variety, and depth was conducted for 2019–2024
► The wholesale and retail pricing categories of HMs were identified along with their year-to-year dynamics, determining a broad price range
► Supplier countries of HMs were identified and the market share of manufacturers dominating the Azerbaijani homeopathic sector was determined
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The presented information can be used by physicians when assessing the availability of HM pharmaceutical forms on the pharmaceutical market of Azerbaijan
► The obtained data will assist physicians in making prescription choices during consultations, which will increase the demand for HMs in clinical practice and enhance pharmaceutical provision
► The results of the study may serve as a basis for further research on the clinical effectiveness of HMs in local settings as well as stimulate domestic production
Objective: To study the dynamics and characteristics of the market of homeopathic medicines (HMs) in Azerbaijan for the period 2019–2024.
Material and methods. Official information of the Ministry of Health, the Tariff Council of the Republic of Azerbaijan and the Biological Medicine Clinic on the volume of HM receipts for the period specified was studied. The following key aspects were analyzed: HM product range indicators (breadth, variety, and depth); countries-producers and suppliers; the level of wholesale and retail prices for HMs. Forecasted indicators for the breadth, variety, and expected volume of homeopathic medicines for the year 2025 were calculated.
Results. Data for the 2019–2024 period demonstrated relative stability in the breadth, variety, and depth of the range of HMs in the pharmaceutical market of Azerbaijan. The forecasted breadth and variety of the HM range in 2025 was estimated at around 96 items and 408 positions, respectively. The range depth remained constant throughout the study period (p=0,928). The forecasted sales volume of HMs in 2025 reached 4.92×106 USD. The highest number of registered HMs was recorded in 2016 (effective date of registration of these drugs). Since then, the number of registrations was decreasing year by year, reaching single cases in 2023–2024. During 2019–2024, the dynamics of the most in-demand pharmaceutical form – soluble tablets – followed a non-linear trend (p=0.076). The dynamics of the market share of products supplied by the leading manufacturer Biologische Heilmittel Heel GmbH (Germany) during the study period demonstrated a nonlinear trend (p=0.994). Similarly, the trend in the market share of products supplied by Materia Medica Holding (Russian Federation) was also nonlinear; however, statistically significant differences were observed from 2019 to 2024 (p<0.001). Throughout the period under study, the HM market was dominated by products into the wholesale price range of 1.17 to 5.88 USD, and the share of these products remained largely unchanged (p=0.766). No statistically significant differences were observed in the distribution of retail price segments for HMs over the study period (p=0.882).
Conclusion. HMs have maintained their niche in the Azerbaijani market year after year, and their availability ensured through imports and an established distribution system.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (ω3-PUFAs) exhibit anti-inflammatory, cardio-, hepato- and neuroprotective properties, they can inhibit the iron-dependent form of apoptosis (ferroptosis) of hepatocytes
► Micronutrient and pharmaceutical ω3-PUFA preparations are used to provide cardioprotection as well as to prevent atherosclerosis, endotheliopathy, chronic inflammation, and thrombophilia; they are also used for neuroprotection and immune support
► Preparations with insufficient standardization and purification from impurities provoke oxidation and tissue aging
What are the new findings?
► A new D-galactose model of aging was first tested, reinforced by dietary components that cause both tissue aging and multiple organ pathology (palm oil, L-methionine, sodium chloride, ferrous sulfate)
► All studied samples of ω3-PUFAs significantly normalized abnormally elevated chronic inflammation (normalization of leukocyte levels, decrease in erythrocyte sedimentation rate), reduced the percentage of large erythrocytes; a trend towards a decrease in originally elevated blood level of ferritin was revealed
► Preparations of ω3-PUFAs contributed to the restoration of normal neurological condition (increased activity in the open field and Porsolt tests), thereby slowing down the age-related decline in cognitive abilities
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The use of pharmaceutically standardized ω3-PUFA preparations slows down multiple organ pathology while protecting the liver from the destructive effects of the accelerated dietary aging, thus providing prospects for clinical research in this area
Background. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (ω3-PUFAs) exhibit anti-inflammatory, cardio-, hepato- and neuroprotective properties that can be beneficial in counteracting the pathophysiology of aging.
Objective: To study the effects of standardized ω3-PUFA intake on a model of accelerated “dietary” aging caused by D-galactose in combination with palm oil and L-methionine in the diet, sodium chloride in drinking water, as well as ferrous sulfate.
Material and methods. The experimental testing of three pharmaceutically standardized ω3-PUFA preparations (NFO® Omega-3 Ultima, NFO® Omega-3 Strong DHA, NFO® Omega-3 Premium) was conducted on the developed aging model. The model was reproduced up to Day 13 of the experiment; after Day 13, all animals were switched to a standard diet that was supplemented with ω3-PUFA preparations until Day 54 of the experiment. On Days 0, 13, and 54, the animals were assessed for 55 indicators, including the results of a complete blood count, blood chemistry, and neurological testing.
Results. All studied ω3-PUFA preparations had a positive effect on 23 of 55 indicators in the animals with the aging model. In particular, standardized ω3-PUFAs helped inhibit liver tissue degradation (normalization of serum vitamin B12 levels to 100±1 pg ml; control: 380.5±29.04 pg/ml; p=0.0005), restore liver function (increase in abnormally decreased direct bilirubin to 1.5±0.1 μmol/l; control: 0.79±0.4 μmol/l; p=0.00363) and folate levels (41.53±6.65 nmol/l; control: 26.82±5.99 nmol/l; p=0.00123). Moreover, ω3-PUFAs prevented a sharp drop in iron levels by Day 54 (54.52±21.03 μmol/l; control: 26.98±1.16 μmol/l; p=0.01185), inhibited the development of hypernatremia (125.47±1.16 mmol/l; control: 141.42±1.3 mmol/l; p=0.0001), and hyperkalemia (5.83±0.23 mmol/l; control: 7.29±0.05 mmol/l; p=0.00001). The study results were histologically confirmed.
Conclusion. All studied omega-3 PUFA samples normalized abnormally elevated chronic inflammation in the animals thereby contributing to the restoration of their normal neurological status. Thus, the use of standardized ω3-PUFAs in inhibiting the pathophysiology of aging is promising.
REVIEW ARTICLES
What is already known about thе subject?
► Fixed-dose combinations (FDCs) of prostaglandins and timolol effectively lower intraocular pressure with good tolerability in glaucoma and ocular hypertension
► FDCs of travoprost/timolol (ТТ) and latanoprost/timolol (LT) are routinely used, yet direct pharmacoeconomic comparisons are scarce
► Existing studies highlight cost differences and side effect profiles of specified FDCs, but no systematic syntheses are available
What are the new findings?
► The first systematic review focusing on the cost-effectiveness of TT- vs. LT-FDCs in glaucoma therapy was conducted
► Global data on clinical efficacy, safety, and economic outcomes of both FDCs were integrated
► PRISMA-based methodology and cost analysis were employed, strengthening evidence quality
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The data obtained facilitate evidence-based decision-making by factoring in cost along with clinical efficacy when selecting glaucoma therapy
► The results of the review help optimize the allocation of resources in the context of a limited healthcare budget
► The information provided can be used to update formularies and clinical guidelines toward more cost-effective regimens
Background. Primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) is a chronic, progressive eye condition causing optic nerve damage and irreversible vision loss by increasing intraocular pressure (IOP). Therapy primarily aimed at reducing IOP to prevent disease progression. Pharmacoeconomic evaluation of fixed-dose combinations (FDCs) has attracted growing interest in recent years as a strategy to enhance both treatment efficacy and accessibility.
Objective: To review the cost and clinical effectiveness for FDCs of travoprost/timolol (TT) and latanoprost/timolol (LT) for POAG treatment.
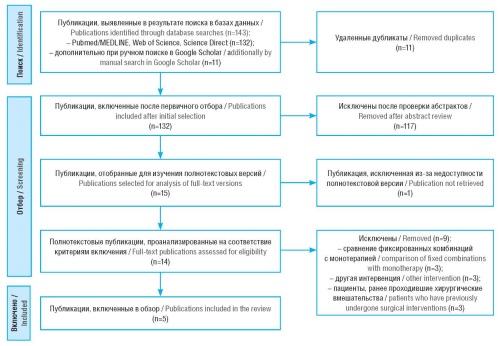
Material and methods. A systematic literature review was conducted using PubMed/MEDLINE, Web of Science, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar databases. The sampling included studies evaluating FDCs of TT and LT in terms of its cost and clinical effectiveness, as well as cost-effectiveness and cost-utility ratios.
Results. TT-FCD proved to be more cost-effective than LT-FDC in several European countries and the Philippines, resulting in lower long-term costs and slowing the progression of vision loss. Conversely, in China identified LT-FDC was more cost-effective due to lower daily costs. Both FDC options improved patient adherence to treatment due to their simplified administration.
Conclusion. TT-FCD may be a more favorable treatment option for POAG in certain regions, considering its pharmacoeconomic and clinical advantages. However, treatment selection should be individualized based on regional healthcare dynamics, medicine pricing, and patient access to medicines.
What is already known about thе subject?
► Artificial intelligence (AI) is widely used in oncology for medical image analysis, diagnosis, personalized treatment, and outcome prediction
► AI technologies including IBM Watson for Oncology and Google DeepMind have proven their efficiency in clinical decision support
► AI facilitates the analysis of large volumes of clinical data, the identification of patterns, and the improvement of clinical decision-making
What are the new findings?
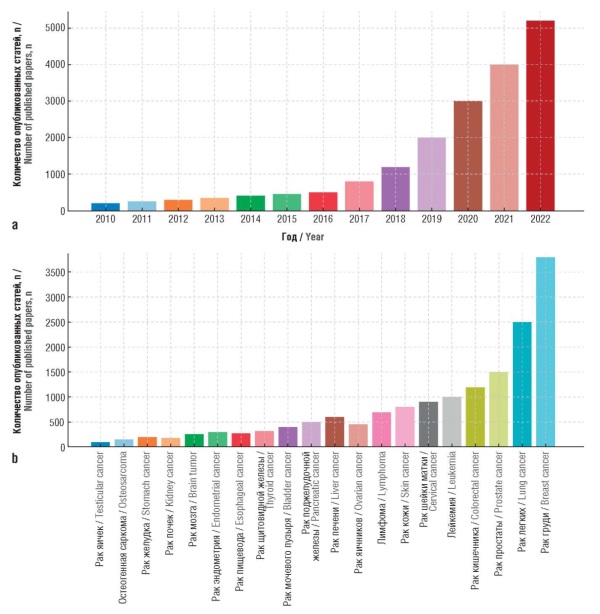
► An analysis of foreign experience in the application and integration of AI in oncological practice from 2000 to 2025 was conducted
► Current AI technologies were reviewed, along with publication trends and AI model developments, which indicate the prospects for designing smart hospitals and improving data exchange
► Innovative features such as wearable integration, multimodal analysis (images + genomics), and consultation automation were detected; potential challenges, including data bias, privacy, and regulatory barriers were determined
How might it impact the clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► AI will reduce diagnostic time and improve the accuracy of tumor detection, particularly at early stages
► AI-driven personalized treatment approaches will improve clinical outcomes and reduce the frequency of side effects
► The integration of AI into clinical practice will enhance the efficiency of healthcare providers and reduce their workload
Objective: To analyze foreign experience in the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in oncology, as well as examine current advances in AI and its impact on clinical practice.
Material and methods. A systematic review of foreign literature was carried out, current AI programs and technologies in oncology were analyzed. The total number of identified records via the PubMed/MEDLINE search was 7680. After publication selection in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines, 32 studies that met all criteria were randomly included in the review and formed the basis for the analysis.
Results. AI demonstrates high efficiency in cancer diagnostics, including early detection of tumors, analysis of medical images and pathological data. A literature review on the use of AI models in oncology revealed exponential growth from 2010 to 2022, confirming the active development of the field. Diagnostic and treatment reports generated by the AI technologies indicated a comparable level of accuracy to that of experienced oncologists; they also revealed the ability to improve clinical outcomes. Furthermore, the introduction of AI stimulates the development of personalized treatment, increased patient adherence to therapy and optimization of the work of medical organizations. AI’s impact was revealed on physicians (reduced diagnostic and treatment errors), patients (personalized support), and hospitals (smart management systems).
Conclusion. AI is becoming an integral part of modern oncology, offering new opportunities to improve diagnostics, treatment, outcome prediction, and patient support. A study of the dynamics of publications and AI models indicates that the use of AI in clinical oncology is rapidly developing, opening up new prospects for the creation of smart hospitals, simplification of medical data exchange, development of personalized medicine, and improvement of the quality of patient care. The integration of AI with emerging technologies such as wearable devices and multimodal analysis promises to revolutionize oncology practice.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
ISSN 2070-4933 (Online)